SimpleBGC Gimbal (aka AlexMos gimbal)¶
The SimpleBGC is a popular brushless gimbal controller that can communicate with ArduPilot (Copter, Plane, and Rover) using a custom serial protocol. More details on the capabilities of this gimbal can be found at basecamelectronics.com
Note
Support for this gimbal is included in Copter 3.4 (and higher).
Where to Buy¶
The SimpleBGC controller and accompanying 2-axis and 3-axis gimbals can be purchased from basecamelectronics.com and many other retailers.
Connecting the gimbal to the Flight Controller¶
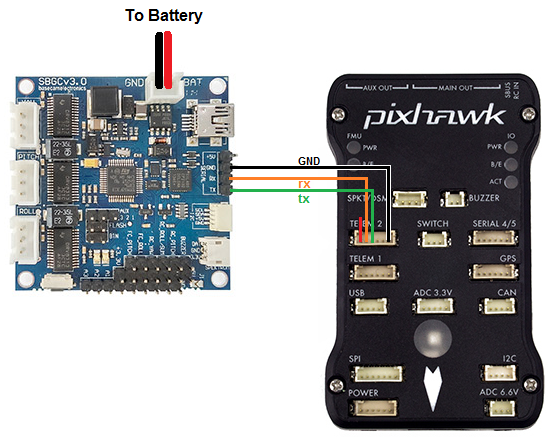
Although the SimpleBGC can be connected using PWM (similar to the Tarot gimbal) we recommend using the serial interface connected to one of the flight controller’s Serial/Telemetry ports like Telem2 as shown above.
In Ardupilot/APM Planner/Mission planner set the following variables:
- MNT_TYPE to 4 / “Mount Type (None, Servo or MavLink)”
- SERIAL2_PROTOCOL to 1 / “MavLink” (Notee “SERIAL2” should be “SERIAL1” if using Telem1 port, SERIAL4 if using Serial4/5, etc)
- SR2_EXTRA1 to 20
- SR2_POSITION to 10
- SR2_RC_CHAN to 20 and all other SR2_* variables to 0.
If you wish to control the pitch angle manually you can set:
- MNT_RC_IN_TILT to 6
- In the SimpleBCG GUI in the tab “RC Settings” in the field “Input Configuration” set PITCH to “API_VIRT_CH6”.
Warning
If you connect the gimbal as shown in the above diagram, it is NOT possible to establish a connection to the GUI on a PC via USB and have it connected simultaneously to the flight controller. It happens because the UART1 (“serial” in the picture above) is “paralleled to the onboard USB-UART converter (excepting the “Tiny” boards that has a dedicated USB). If you accidentally connect both the GUI via USB and a flight controller via UART1, you might end up with corrupt data on the flash of the gimbal. It can result in unexpected motor movement! The reason details, please check the link .
Setup through the Ground Station¶
Set the following parameters through your ground station and then reboot the flight controller:
- MNT_TYPE to 3 / “AlexMos-Serial”
- SERIAL2_PROTOCOL to 7 / “AlexMos Gimbal Serial” (Notee “SERIAL2” should be “SERIAL1” if using Telem1 port, SERIAL4 if using Serial4/5, etc)
If you are unable to connect you may wish to set the following parameters although normally this should not be required:
- SERIAL2_BAUD to 115 (means use serial baudrate of 115200)
- BRD_SER2_RTSCTS to 0 to disable flow control on Telem2 (use BRD_SER1_RSCTS if connecting to Serial1, Serial4/5 never uses flow control)
The gimbal’s maximum lean angles can be set using these parameters:
- MNT_ANGMIN_ROL, MNT_ANGMAX_ROL to -3000 and 3000 to limit the roll angle to 30 degrees in each direction
- MNT_ANGMIN_TIL, MNT_ANGMAX_TIL to -9000 and 0 to limit the gimbal to point between straight down (-90 degrees) and straight forward (0 degrees)
To control the gimbal’s lean angles from a transmitter set:
- MNT_RC_IN_TILT to 6 to control the gimbal’s tilt (aka pitch angle) with the transmitter’s Ch6 tuning knob
For a 3-axis gimbal with 360 degrees of yaw set:
- MNT_ANGMIN_PAN, MNT_ANGMAX_PAN to -18000 and 18000 to get a full 360 degrees of yaw range
Using Gimbal GUI and MavLink Connection¶
To use the gimbal GUI and the flight controller with MavLinkis necessary to use of the Gimbal firmware version 2.60 or above is also needed.
The following instructions present how to wire the components:
- Connect the flight controller as shown above but connect the RX wire (orange) to the RC-R and the TX wire (green) to the RC-Y pin on the gimbal
- Connect the ground wire (black) to any GND pin.
In this setup you have to take care of the following options in the GUI:
- Activate RC_SERIAL by setting “RC_ROLL pin mode” = “Serial port (Serial API, etc.)” on the RC tab On the tab “External IMU” in the field “External IMU configuration”
- Select the Model: “MavLink FC channel 1”
- Connection: disabled On the same tab in the field “MavLink connection” for Channel 1 (leave Channel 2 disabled)
- Serial port: “RC_serial” - System Id/Component Id: 1, 154
- Port setting: 115200, none parity
- Check the options: Send heartbeat and Query RC data
- MavLink control mode: “Controls ROLL and PITCH axes only” If everything is set correctly you should see something like the following in the fields: AHRS: OK (40ms), GPS: OK (106ms), RC: OK, Control: OK CH1: Packets received: 257502, lost: 0, parse errors: 3 CH2: Packets received: 0, lost: 0, parse errors: 0.
Testing the gimbal moves correctly¶
Testing the pilot’s control of pitch
Once powered the gimbal should point to it’s Tilt Angle Min (i.e. straight down) when your transmitter’s channel 6 tuning knob is at its minimum PWM value (perhaps around 1000) and the camera should point to its maximum tilt angle (i.e. straight forward) when the tuning knob is at its maximum (perhaps around 2000). The Mission Planner Radio calibration page can be used to check the Ch6’s current input PWM value.
Testing ROI
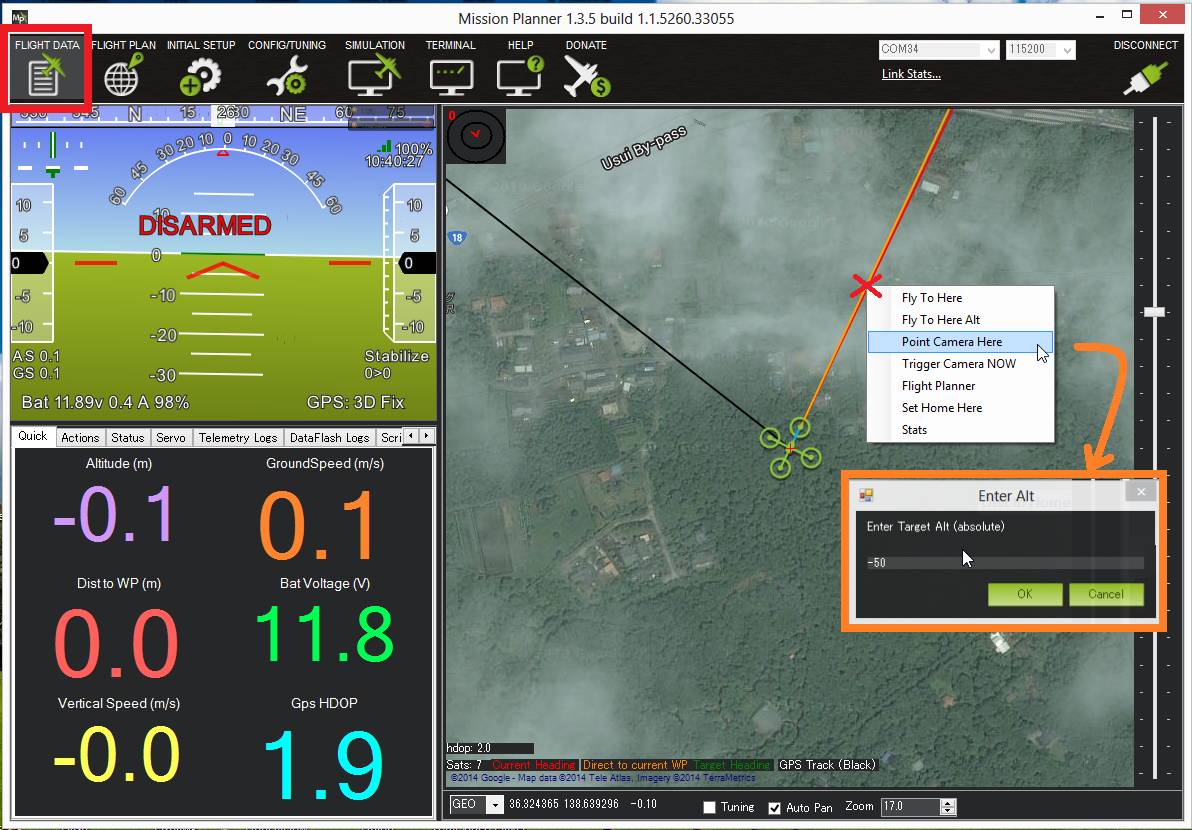
You must have GPS lock to test ROI. The ROI feature points the vehicle and/or camera to point at a target. The instructions above describe setting up the APM/Pixhawk so that it only controls the Tilt (i.e. pitch) of the Tarot gimbal so when a Do-Set-ROI command is received Copter will attempt to turn the vehicle’s nose to point in the direction of the target and tilt camera depending upon the vehicle’s distance and altitude. You can test the gimbal tilt moves correctly by connecting with the mission planner, then on the Flight Data screen’s map, right-mouse-button-click on a point about 50m ahead of the vehicle (the orange and red lines show the vehicle’s current heading), select Point Camera Here and input an altitude of -50 (meters). This should cause the gimbal to point down at about 45 degrees.