LIDAR-Lite Rangefinder¶
The Garmin / PulsedLight LIDAR-Lite rangefinder is a low-cost optical distance measurement solution with a 40m range under most operating conditions, low power consumption, and small form factor. This sensor can be purchased from Sparkfun and these distributors and then technical info can be found here.
Note
This rangefinder is only supported on the following vehicle platform versions (or later): Copter 3.3, Plane 3.3, and Rover 2.49. ArduPilot transparently supports both LIDAR-Lite v1 and v2.
Problems with the Lidar-Lite v2¶
A number of problems have been found with the Lidar-Lite v2. Attempts to resolve these issues with the developers of the product have not been entirely successful. These notes serve as a warning to potential users. It is not yet clear if these issues have been resolved in v3.
The problems are:
- lockups when using I2C with the older “black-label” Lidars
- GPS interference with the older “black-label” Lidars
- interference with other I2C devices when using “blue-label” Lidars
- a 13m offset from true distance on both “blue-label” and “black-label” Lidars
Lockup on I2C¶
The first issue (lockups on I2C with black-label lidars) is solved by either using the new blue-label Lidars or by using the PWM output method, preferably with a reset pin. The issue is not common, but it is relatively easy to reproduce in bench tests by covering the Lidars lenses. It appears to be more likely to happen when the Lidar is reading short distances. There are two manifestations of the issue - one is where the lockup is solved by sending a I2C reset command, the the other does not respond to an I2C reset.
GPS Interference¶
The older black-label Lidars cause significant GPS interference. This manifests as longer time to get GPS lock on power up and higher levels of GPS noise when lock is achieved resulting in lower GPS accuracy. Testing shows that the interference includes both a conducted and radiated component.
Placing the Lidar as far away from the GPS as possible helps, but does not entirely eliminate the issue.
Note that the GPS interference problem does not happen with the newer “blue-label” Lidars.
I2C interference with blue-label Lidars¶
The newer blue-label Lidars have been associated with interference problems on I2C with other I2C devices on the same bus. In particular, incorrect airspeed readings have been seen when used on the same I2C bus as a digital airspeed sensor. This issue does not occur in all aircraft, but when it does occur the results are quite dramatic, with airspeed readings being off by more than 10m/s.
Although bench testing has reproduced the result we have not yet managed to capture a logic trace of it happening. The problem is solved by using the Lidar via PWM instead of I2C.
A 13m offset on all Lidars¶
Both the newer blue-label and older black-label Lidars have a problem where they will sometimes return a distance of approximately 13m greater than the true distance. This happens on both I2C and PWM. The problem is rare, but it has been recorded in several flight logs on several different aircraft. The problem has also been reproduced in extensive bench testing.
When the problem happens the 13m offset usually locks in place, so all remaining readings from the Lidar for the rest of the flight will give a 13m offset. There have however been cases where the 13m offset disappears after a few seconds or minutes.
The problem is much more likely to occur if the Lidar power supply fluctuates too much. The problem can be easily reproduced in a bench setup where the Lidar is initially powered at below 4V then the voltage raised.
Unfortunately low supply voltage is not the only trigger for the problem, so ensuring a good power supply will reduce the probability of the issue but not eliminate it. Multiple flight logs where the supply voltage to the Lidar is being monitored show the problem can occur with a good power supply.
There is no known workaround for this issue. Detailed traces of the issue have been provided to the makers of the device with no resolution. The issue has also been reproduced using the device makers own software and own recommended hardware setup.
Connecting to the Pixhawk via I2C¶
Warning
If you have a LIDAR-Lite that has a manufacture date label prior to February 2015 there are I2C interface communications issues that will cause unreliable operation of the sensor with Pixhawk and will cause your vehicle to crash. When using these versions of LIDAR-Lite please use the PWM alternative listed below for best results.
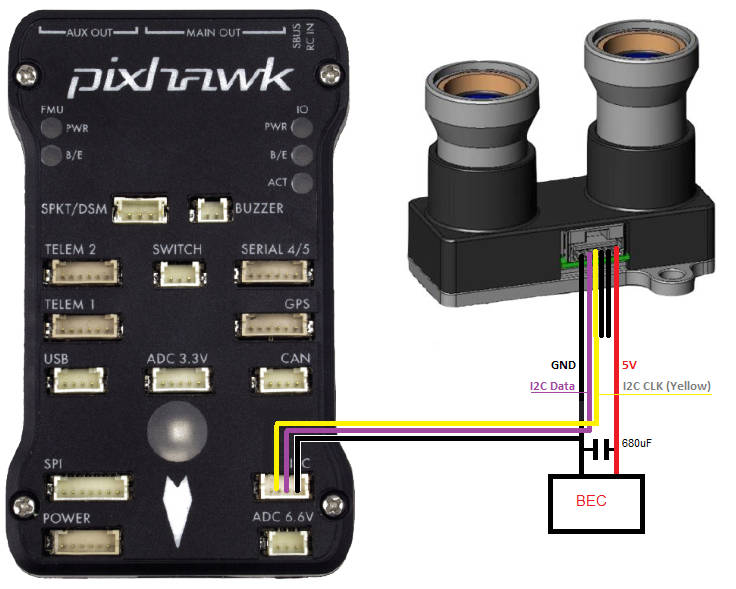
The cable is configured with a 6-position Molex CLIK Mate connector on one end and tinned leads on the opposite end. You will need to solder the tinned ends to a modified DF13 4-pin I2C cable as shown below.
The power to the rangefinder should be supplied from a separate external BEC as shown in the diagram below.
Note
The low pass filter shown in the diagram is required for first generation hardware (for hardware with manufacture dates prior to February 2015) - a schematic and PCB design are provided here. These should not be required in later versions of the LIDAR Lite (at which point the diagram will change as shown below:
You may wish to also purchase an I2C splitter so that you can continue to connect an external GPS/Compass module.
Note
It is important to ensure that the ground from the BEC is connected to the ground on the servo rail.
Connecting to Pixhawk via PWM¶
As of the 3.3.x release of Plane and Copter you can connect your Lidar via PWM as an alternative to I2C. This works around a number of bugs in the I2C interface for the Lidar. The bugs include generating spurious pulses on the I2C bus and lockups of the Lidar in flight.
To connect via PWM you need to connect 4 pins on the Lidar to the PWM rail of the Pixhawk. The connections are as follows:
| LIDAR-Lite Pin | Pixhawk Pin |
| J1 | CH6 Out V+ |
| J2 | CH6 Out Signal (internal pin 55) |
| J3 | CH5 Out Signal (internal pin 54) |
| J4 | (not used) |
| J5 | (not used) |
| J6 | Ch6 Out Ground |
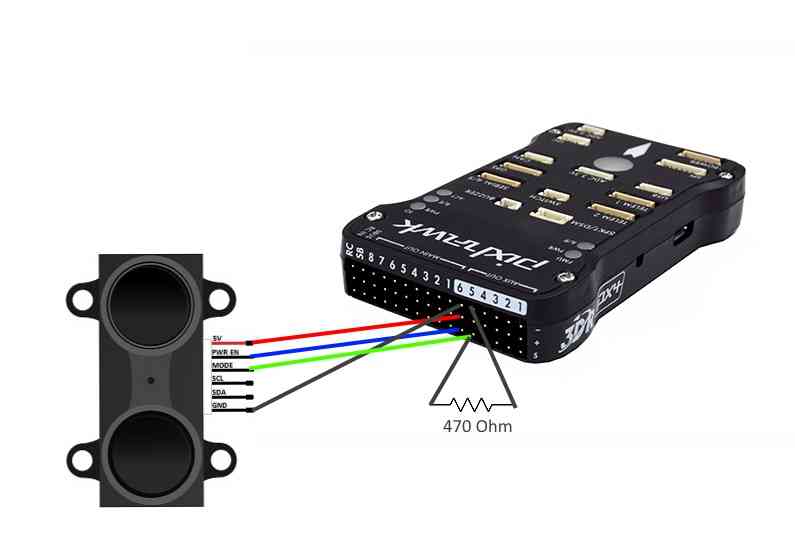

You need a resistor between J3 and ground. The exact value of the resistor isn’t critical, somewhere between 200 Ohm and 1kOhm will do. Testing for the development of the driver was done with a 470 Ohm resistor. The resistor is what tells the Lidar to start taking a reading, so connecting a resistor between pin 3 and ground tells the Lidar to go into continuous acquisition mode.
Here’s a picture of the necessary cable, with the resistor shown before being covered by heat-shrink tubing:

You then need the following parameters set to enable the PWM driver:
RNGFND_TYPE= 5RNGFND_STOP_PIN= 55BRD_PWM_COUNT= 4RNGFND_SCALING= 1RNGFND_OFFSET= 0
Note: For RNGFND_SCALING your mileage may vary. Some units work better using RNGFND_SCALING=0.8.
The use of pin 55 as the stop pin is just a suggestion, not a requirement. It connects to the enable pin on the Lidar, and allows the driver to reset the Lidar if it stops providing readings.
The use of pin 54 for the PWM signal is required, and only FMU AUX5 (pin 54) can be used due to the internal timer routing of the Pixhawk.
Note: when using LIDAR-Lite in PWM mode please keep the following in mind:
- You need to have a battery/ESC plugged in. (in PWM mode, the LIDAR-Lite gets its power from the servo rail, which is powered by the ESC)
- On the ground station side, APMPlanner currently does not display the data, but Mission Planner does. Fixes are on the way.
- Make sure the LIDAR is not right on a table and is at least 20cm or so from the nearest surface. Otherwise, it will display 0 distance (which is correct!)
- By default, on Copter if you have the LIDAR enabled, it will check LIDAR range on startup. To pass the check, lift the vehicle up at least 50cm. Don’t tip it over too much because the check is a bit sensitive, it needs to see a range of between 50cm ~ 2m but nothing longer than 2m. If it sees a range longer than that, it’ll never pass unless you reboot the board (nicer solution to this coming soon!). The check can be disabled by setting ARMING_CHECK to Skip Param/Sonar.
Optional Power Saving¶
When using the PWM driver you can optionally set RNGFND_PWRRNG to a
terrain height in meters above which the Lidar will be disabled to save
power. When the terrain data indicates that the vehicle is above that
height the RNGFND_STOP_PIN will be used to disable the Lidar. This
saves around 100mA of current.
Your GCS must provide terrain data for this to work.
Setup in Mission Planner¶
To configure Copter, Plane or Rover to use the LIDAR-Lite:
Connect with the Mission Planner and open the Config/Tuning | Full Parameter List page.
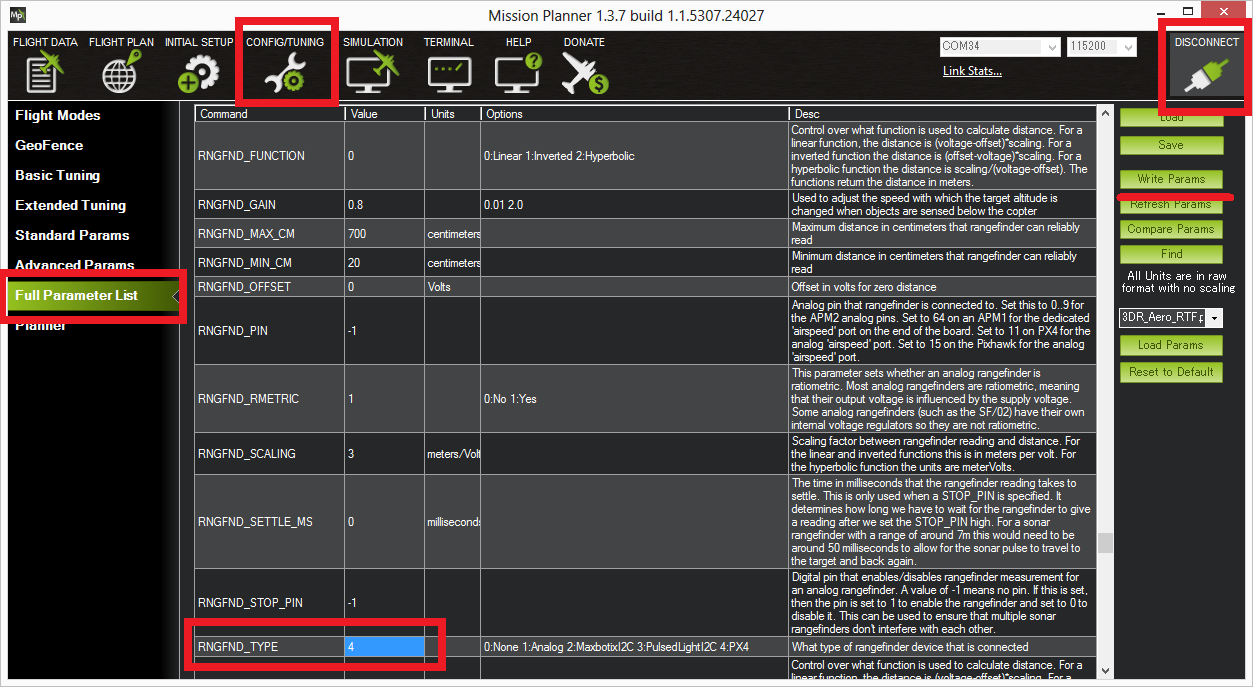
Set the
RNGFND_TYPEvalue based on the flight controller and connection method (PWM or I2C):RNGFND_TYPE=5: Pixhawk via PWMRNGFND_TYPE=4: Pixhawk via I2CRNGFND_TYPE=3: APM2 via I2C
Set the
RNGFND_MAX_CMto 4000 (40m). This parameter represents the maximum distance in centimeters that the LiDAR is reliable over — when ignoring “0” distance readings in the driver, a value of 4000 should work well in almost all conditions.Set
RNGFND_MIN_CMto 20cm. Below that distance you will still get readings, but they may be inaccurate (the optics can start to introduce parallax error if the sensor picks up signal from specular reflections rather than directly from a return signal).
Testing the sensor¶
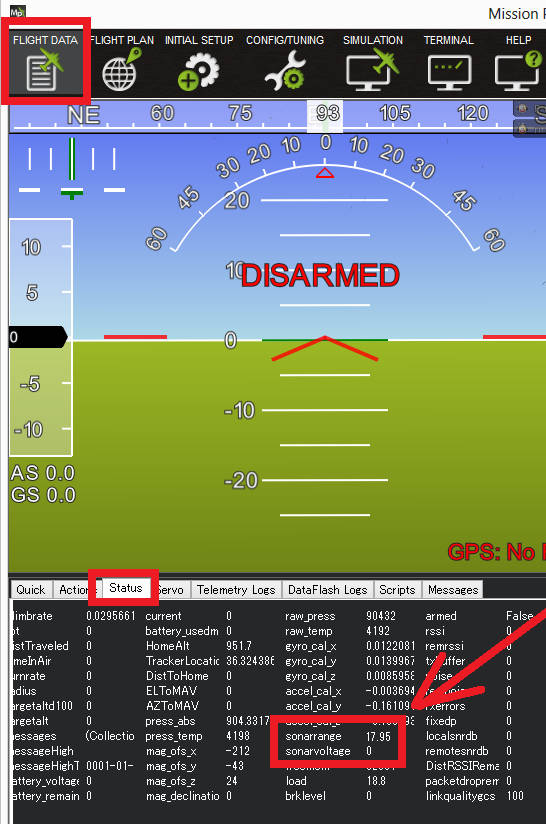
Distances read by the sensor can be seen in the Mission Planner’s Flight Data screen’s Status tab. Look closely for “sonarrange”. Its best to place the Lidar several known distances (1m, 3m, 5m) from a large flat wall to test it. If the Lidar is constantly reading wrong by a fixed offset e.g. its always 50cm out at each distance then adjust the RNGFND_OFFSET parameter by the correct amount. If however it gets the distance wrong each time by a different amount then the RNGFND_SCALING parameter needs changing. Update it (maybe 1.1 or 0.9) and test again and repeat until its correct.
Video guide¶
The following video guide also shows how to set up the LIDAR-Lite (referencing this wiki article):

